- Rachel Feltman at the Washington Post, "Calculus apprehensions may steer women away from science careers," who began her piece with her own experience, “Calculus II was one of the most demoralizing experiences of my college career.”
- Dominique Mosbergen at the Huffington Post, "This Popular Math Class Is At The Heart Of The STEM Gender Gap, Study Suggests"
- Lauren Camera at U.S. News, "Calculus Steers Women Away From STEM"
- Maggie Kuo at Science, "Low math confidence discourages female students from pursuing STEM disciplines"
The article was an outgrowth of the “switcher” analysis that Jess Ellis and Chris Rasmussen had begun, using data from our 2010 national survey to study who came into Calculus I with the intention of staying on to Calculus II but then changed their minds by the end of the course. You can find a preliminary report on the Ellis and Rasmussen switcher analysis in my column for December 2013, MAA Calculus Study: Persistence through Calculus and a further analysis of the differences between men and women in the November, 2014 column, MAA Calculus Study: Women are Different. See also Rasmussen and Ellis (2013).
The 2013 column reported that women were about twice as likely as men to switch out of the calculus sequence, but those data were compromised by several lurking variables, most significantly intended major. Women are heavily represented in the biological sciences, much less so in engineering and the physical sciences. Since the biological sciences are less likely to require a second semester of calculus, some of the effect was almost certainly due to different requirements.
The study published in PLOS One controlled for student preparedness for Calculus I, intended career goals, institutional environment, and student perceptions of instructor quality and use of student-centered practices. They found that even with these controls, women were 50% more likely to switch out than men. As I discussed in my 2014 column, while Calculus I is very efficient at destroying the mathematical confidence of most of the students who take it, it is particularly effective for women (see Figure 1). As Ellis et al. report, 35% of the STEM-intending women who switched out chose as one of their reasons, “I do not believe I understand the ideas of Calculus I well enough to take Calculus II.” Only 14% of the men chose this reason.
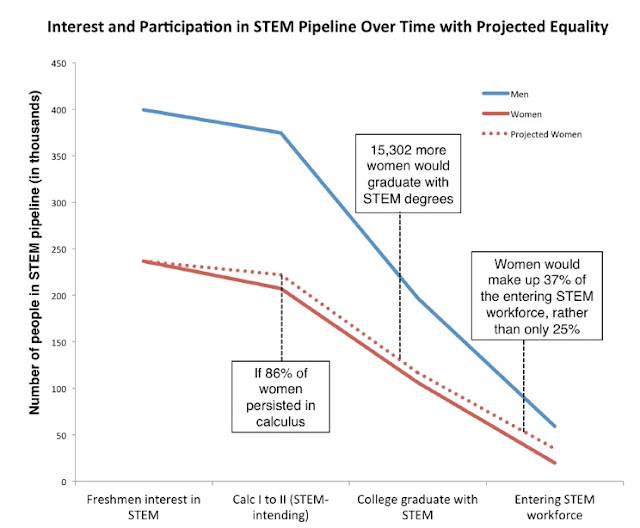
The last figure in the Ellis et al. article is enlightening (see Figure 2). If we could just raise the persistence rates of women once they choose enter Calculus I to match that of men, we could get a 50% increase in the percentage of women who enter the STEM workforce each year.
I believe that this issue of women’s confidence is cultural, not biological. It fits in with all we know about stereotype threat. When the message is that women are not expected to do as well as men in mathematics, negative signals loom very large. Calculus—as taught in most of our colleges and universities—is filled with negative signals.
Reference
Ellis, J., Fosdick, B.K., and Rasmussen, C. (2016). Women 1.5 times more likely to leave STEM pipeline after calculus compared to men: Lack of mathematical confidence a potential culprit. PLoS ONE 11(7): e0157447. doi10.1371/journal.pone.0157447
Rasmussen, C., & Ellis, J. (2013). Who is switching out of calculus and why? In Lindmeier, A. M. & Heinze, A. (Eds.). Proceedings of the 37th Conference of the International Group for the Psychology of Mathematics Education, Vol. 4 (pp. 73-80). Kiel, Germany: PME.